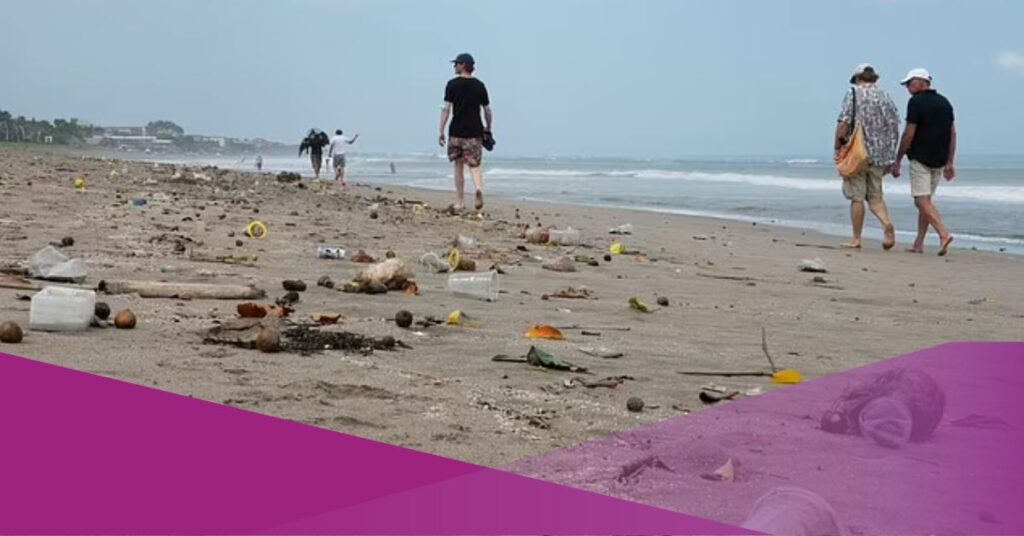
A nonprofit organisation in Bali has been monitoring the water quality at two of the island’s most popular tourist beaches. According to the tests’ findings, the seawater in Canggu’s Batu Bolong Beach and Seminyak’s Petitenget Beach is contaminated with harmful E.coli bacteria.
Yayasan Bali Bersih, a Bali-based nonprofit affiliated with the Westerlaken Foundation in the Netherlands, has been performing water quality assessments at Bali’s busiest beaches destinations whichresults are surprising.
Through their Instagram accounts, Yayasan Bali Bersih (the Clean Bali Foundation) and the Westerlaken Foundation have shared their findings with the general public. The organisations conduct routine laboratory testing on seawater as part of regular water quality surveys.
The nonprofit organisation stated that the objective of the research was to “determine whether or not there are Escherichia coli [E, coli] bacteria in seawater, which can disrupt marine ecosystems and potentially endanger the health of locals and beachgoers.”
Yayasan Bali Bersih and the Westerlaken Foundation discovered that E-coli bacteria are present in the ocean after collecting water samples on the 21st of June, 2023. To ascertain the frequency of E. coli in the water samples, the researchers employed the MPS (Most Probable Number Method). According to the results, there were bubbles in the lab test tubes with an MPN of more than 1100.
This indicates the presence of E.coli and seawater contamination in Canggu’s Batu Bolong Beach and Seminyak’s Petitenget Beach. It is concerning because E. coli can be found in water supply and food processing. E.coli contamination is likely due to home or human waste, such as faeces. The high concentrations of E. coli discovered in the water samples last week suggest a danger of the disease spreading among humans due to the bacteria.
According to the researchers, “The inspection results will provide important information to the authorities and the public regarding the condition of clean sea water in Bali.”
The researchers added, “By knowing the content of Escherichia coli in seawater, countermeasures and improvements can be taken to minimise health risks and maintain the sustainability of marine ecosystems.”
Interested in this topic? Check out our other articles from Social Expat: